Trendaavat aiheet
#
Bonk Eco continues to show strength amid $USELESS rally
#
Pump.fun to raise $1B token sale, traders speculating on airdrop
#
Boop.Fun leading the way with a new launchpad on Solana.
The Coming Boom in Crypto Options
Robinhood went all-in on crypto this month, unveiling an @Arbitrum-based L2, rolling out tokenised US equities for anyone with a wallet, and teasing synthetic pre-IPO shares of @OpenAI. However, the first crypto derivative it shipped was perpetuals capped at 3x leverage, not options, which made @RobinhoodApp famous.
This single product choice captures a decade of evolutionary divergence between crypto markets and traditional finance. Traditional markets operate under CFTC constraints that require future rollovers and create operational friction. U.S. regulations cap stock margin leverage at roughly 2x and ban anything resembling "20x perpetuals". Options became the only way for investors with $500 to turn a 1% move in Apple into a 10%+ gain.
This led to explosive growth in the US options market. Nearly half of this activity comes from retail traders punting short-dated options expiring on the same day or by the end of the week. Robinhood built its business around providing quick, easy and free access to options and monetising it via Citadel through a model that’s called payment for order flow.
The Trading Gap
Crypto's unregulated environment, dealing purely in digital assets without physical delivery, created space for innovation. It all began with @Bitmex’s perpetual futures. These futures are unique in that, much like the name suggests, there is no “delivery” date. They are perpetual; you can open a position going up to 100x leverage on any token.
Options are more complex. Investors need to manage multiple variables simultaneously: strike selection, underlying price, time decay, implied volatility, and delta hedging. Most crypto traders evolved directly from spot trading to perpetuals, completely bypassing the options learning curve.
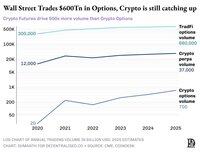
CEXes like @Binance and @Bybit_Official leaned into perpetuals to capture retail demand for leverage. Last month, perp venues cleared roughly US$3.7 trillion in notional value. All crypto options combined cleared just US$100 billion, less than 5% of perp volume.
@DeribitOfficial, the biggest crypto options CEX alone handles 85% of this option flow, highlighting how thin and centralised the market is.
Moving options on-chain looked easy on paper. A smart contract can track strikes and expiries, escrow collateral and settle payouts without middlemen. Yet, after five years of experiments, Option DEXes combined still capture less than 1% of option volume. Compare this to Perp DEXes, which process around 10% of futures volume.
Evolution of On-Chain Options
Options require a counterparty who is willing to take on asymmetric risk. If you bought a BTC call for $100K last year, and the price moved to $115K, the counterparty, known as the option writer, has to pay this $15k out.
They charge a premium based on how likely it is that you might make money, which they calculate using the Black Scholes formula. Higher volatility in the underlying token translates into higher option premia because writers need more compensation for wilder price paths.
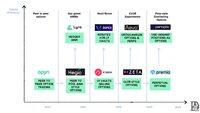
1. The first phase of protocols led by @Opyn_ democratised writing by letting anyone lock collateral and underwrite options as ERC-20s and earn premiums. This let users trade options in a peer-to-peer fashion, but gas fees for minting these options burnt more than the premiums. Writers also had to lock the full notional value until expiry, so capital sat idle for months.
2. Builders next pooled collateral in AMM vaults, inspired by Uniswap’s design. @HegicOptions let traders buy an option with a single click while a pricing curve handled the math. The convenience worked, but the vault mispriced puts; one sharp ETH crash in September 2020 wiped out a year of LP yield and reminded everyone that automated pricing without hedging is dangerous.
3. Lyra (now @Derivexyz) tried to solve that by teaching the vault to hedge net exposure on perpetuals. Hedging cut drawdowns in half, yet the design relied on @Synthetix_io’s DEX liquidity. When the Terra–Luna panic emptied those pools, hedges failed to fill, and option spreads ballooned, making trading impossible.
4. Projects like @RibbonFinance tried underwriting calls as a way to provide yield. Depositors sent ETH to an option vault that auctioned calls expiring in a week. During the bull market, these premiums looked amazing, but when ETH slid, the income no longer covered losses and users were stuck with their positions until expiry.
5. Finally, Solana and Optimism teams such as @PsyOptions, @DriftProtocol,@Aevoxyz and Derive tried to recreate Deribit’s order book, matching trades off-chain and settling on-chain. They onboarded market makers who could prove tight spreads. But makers still had to post fresh collateral for every leg because the smart contracts couldn’t recognise that a short call hedged with spot carries little net risk. Liquidity dried up whenever those makers logged off.
Why Options Struggle
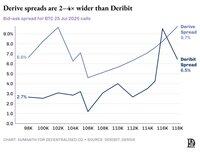
A market-maker selling a $120K BTC call and delta-hedging with spot BTC has near-zero net risk. Deribit recognises that and charges a margin on the combined net exposure. Most on-chain designs tokenise each option in isolation, severing the risk link. Every hedge ties up fresh collateral, so market makers' quotes get wider.
While Derive has partially addressed this by adding perpetuals to enable cross-margin within their clearinghouse, spreads remain significantly wider than Deribit's; often 2-5 times fatter for large positions.
Contrast that with @HyperliquidX, the DEX that now clears about 6% of all perp volumes and matches CEX spreads. Hyperliquid’s secret isn’t novel math; it is plumbing. A single global liquidity pool called HLP sits on the other side of every trade. Traders see one order book, one funding rate, no strike grids and no expiries. The cognitive load is near zero, and the UX is smooth. Longs and shorts take opposite sides of the trade. When net exposure gets lopsided, the protocol’s risk engine hedges on external venues or throttles leverage.
Onboarding new markets is equally painless. Seed a pool, list the asset, and trading can begin without cajoling market makers.
Options, by contrast, splinter liquidity across thousands of micro-assets. Each strike-expiry combination creates its own market with distinct characteristics, dividing available capital and making it nearly impossible to achieve the depth that sophisticated traders require.
Writers’ capital sits frozen until settlement, spreads stay wide, and the seamless UX that powers perps never materialises. This is at the heart of why on-chain options have not taken off.
The Missing Piece
Ironically, the infrastructure that powers Hyperliquid could be exactly what on-chain options have missed. We've written about Hyperliquid's approach to shared infrastructure, creating the positive-sum dynamics that DeFi has long promised but rarely delivered. Every new application strengthens the entire ecosystem rather than competing for scarce liquidity.
We believe that options will finally come on-chain through this infrastructure-first approach. While previous attempts focused on mathematical sophistication or clever tokenomics, HyperEVM solves the fundamental plumbing problem: unified collateral management, atomic execution, deep liquidity and instant liquidation.
There are a few core aspects to changing market dynamics that we see:
1. In the post-FTX crash of 2022, there were fewer market makers in the market engaging with new primitives and taking on risk. Today, that has changed. Participants from traditional avenues have returned to crypto.
2. There are more battle-tested networks that can take on the needs of higher transaction throughput.
3. The market is more open to some of the logic and liquidity not being entirely on-chain.
Options have the Lindy effect and volatility, but are hard for the average individual to understand. We believe there will be a class of consumer apps that focus on bridging this gap, helped along by LLMs that can check premiums and suggest the most attractive strike in plain English.

Read the whole story here:
10,04K
Johtavat
Rankkaus
Suosikit













